2025
Towards Secondary Structure Prediction of Longer mRNA Sequences Using a Quantum-Centric Optimization Scheme
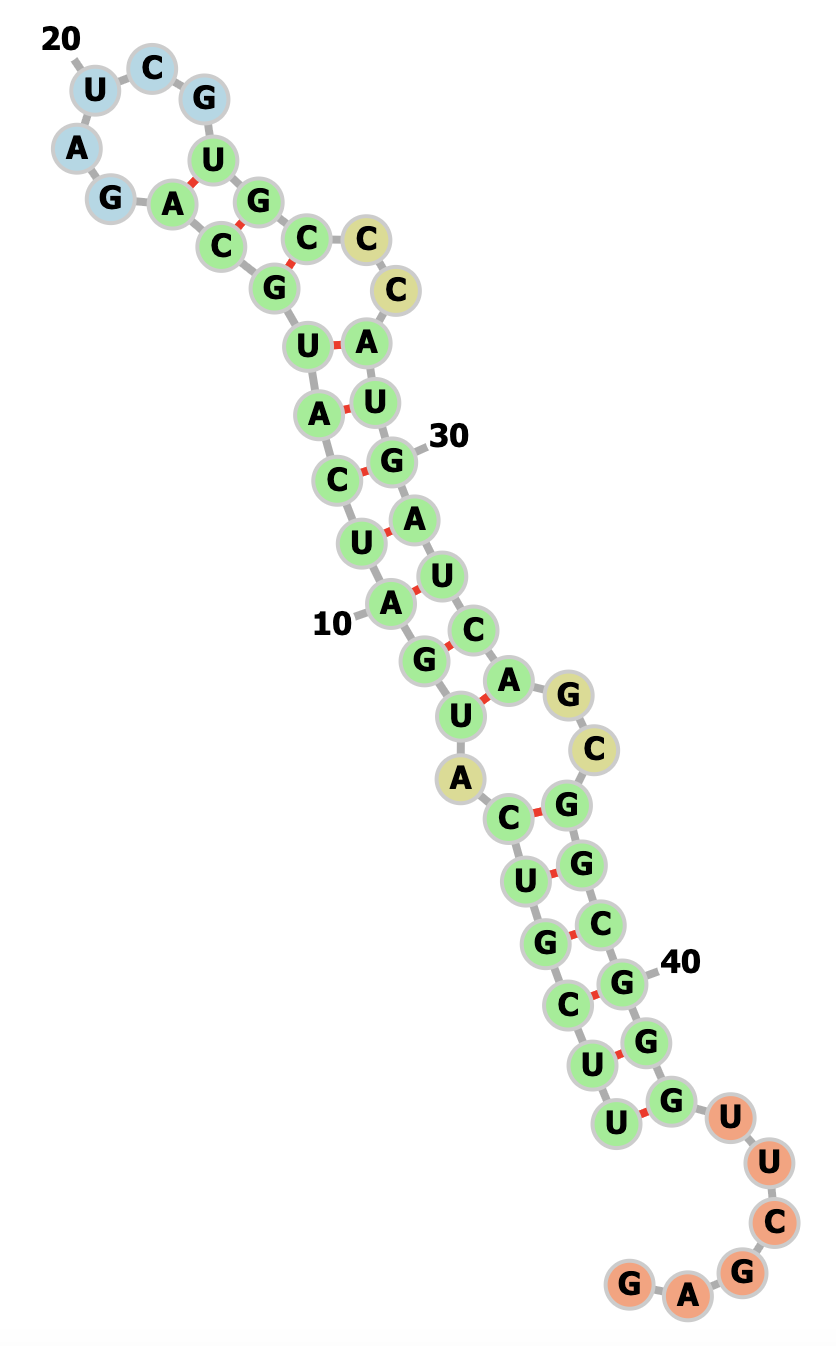
Optimal folded structure of the 60-nucleotide, 150-qubit mRNA sequence based on the corresponding lowest energy bitstring found by the hardware run.
Accurate prediction of mRNA secondary structure is critical for understanding gene expression, translation efficiency, and advancing mRNA-based therapeutics. However, the combinatorial complexity of possible foldings, especially in long sequences, poses significant computational challenges for classical algorithms. In this work, we propose a scalable, quantum-centric optimization framework that integrates quantum sampling with classical post-processing to tackle this problem. Building on a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) formulation of the mRNA folding task, we develop two complementary workflows: a Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR)-based variational quantum algorithm enhanced with gauge transformations and local search, and an Instantaneous Quantum Polynomial (IQP) circuit-based scheme where training is done classically and sampling is delegated to quantum hardware. We demonstrate the effectiveness of these approaches using IBM quantum processors, solving problem instances with up to 156 qubits and circuits containing up to 950 nonlocal gates, corresponding to mRNA sequences of up to 60 nucleotides. Additionally, we validate scalability of the CVaR algorithm on a tensor network simulator, reaching up to 354 qubits in noiseless settings. These results demonstrate the growing practical capabilities of hybrid quantum-classical methods for tackling large-scale biological optimization problems.
Quantum Machine Learning Framework for Longitudinal Biomedical Studies
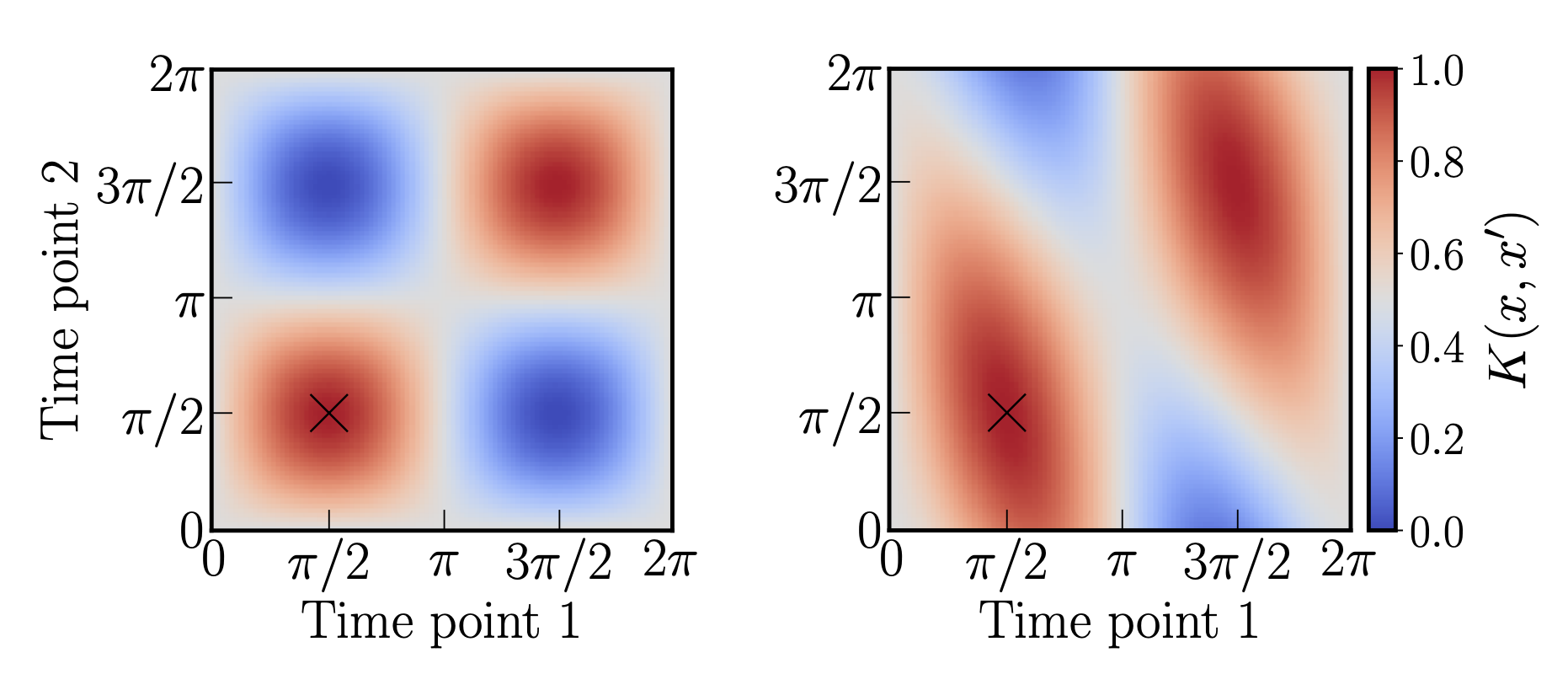
Comparison of the IQP and longitudinal IQP kernels for a two-time-point single-feature setting.
Longitudinal biomedical studies play a vital role in tracking disease progression, treatment response, and the emergence of resistance mechanisms, particularly in complex disorders such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. However, the high dimensionality of biological data, combined with the limited size of longitudinal cohorts, presents significant challenges for traditional machine learning approaches. In this work, we explore the potential of quantum machine learning (QML) for longitudinal biomarker discovery. We propose a novel modification to the instantaneous quantum polynomial time (IQP) feature map, designed to encode temporal dependencies across multiple time points in biomedical datasets. Through numerical simulations on both synthetic and real-world datasets - including studies on follicular lymphoma and Alzheimer's disease - we demonstrate that our longitudinal IQP feature map improves the ability of quantum kernels to capture intra-subject temporal patterns, offering a promising direction for QML in clinical research.
Quantum Machine Learning in Drug Discovery: Applications in Academia and Pharmaceutical Industries
The nexus of quantum computing and machine learning - quantum machine learning - offers the potential for significant advancements in chemistry. This review specifically explores the potential of quantum neural networks on gate-based quantum computers within the context of drug discovery. We discuss the theoretical foundations of quantum machine learning, including data encoding, variational quantum circuits, and hybrid quantum-classical approaches. Applications to drug discovery are highlighted, including molecular property prediction and molecular generation. We provide a balanced perspective, emphasizing both the potential benefits and the challenges that must be addressed.
Accepted in ACS Chemical Reviews
arXiv:2409.15645
2024
mRNA Secondary Structure Prediction Using Utility-Scale Quantum Computers

Optimal folded structure of the 42-nucleotide, 80-qubit mRNA sequence based on the corresponding lowest energy bitstring found by the hardware run.
Recent advancements in quantum computing have opened new avenues for tackling long-standing complex combinatorial optimization problems that are intractable for classical computers. Predicting secondary structure of mRNA is one such notoriously difficult problem that can benefit from the ever-increasing maturity of quantum computing technology. Accurate prediction of mRNA secondary structure is critical in designing RNA-based therapeutics as it dictates various steps of an mRNA life cycle, including transcription, translation, and decay. The current generation of quantum computers have reached utility-scale, allowing us to explore relatively large problem sizes. In this paper, we examine the feasibility of solving mRNA secondary structures on a quantum computer with sequence length up to 60 nucleotides representing problems in the qubit range of 10 to 80. We use Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR)-based VQE algorithm to solve the optimization problems, originating from the mRNA structure prediction problem, on the IBM Eagle and Heron quantum processors. To our encouragement, even with ``minimal'' error mitigation and fixed-depth circuits, our hardware runs yield accurate predictions of minimum free energy (MFE) structures that match the results of the classical solver CPLEX. Our results provide sufficient evidence for the viability of solving mRNA structure prediction problems on a quantum computer and motivate continued research in this direction.
Demonstration of a Parity-Time Symmetry-Breaking Phase Transition Using Superconducting and Trapped-Ion Qutrits
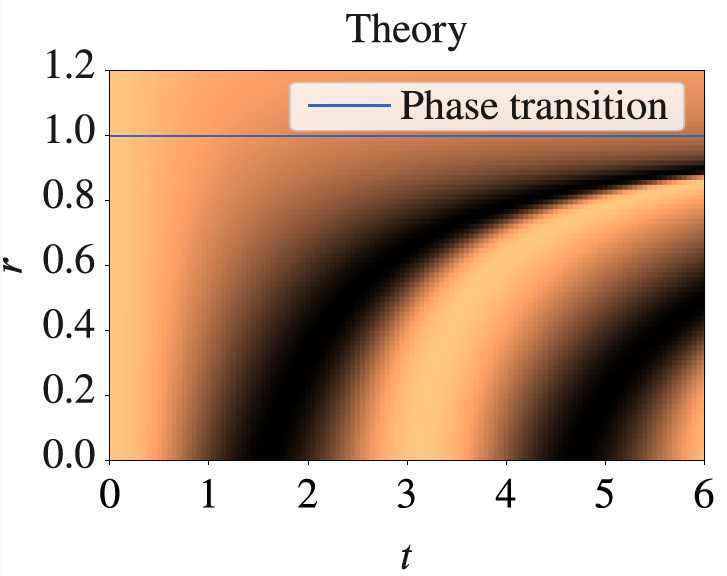
Dynamics of ground state population for a PT-symmetric two-level system.
While being key to understanding many real-world phenomena, simulation of nonconservative quantum dynamics presents a challenge for unitary quantum computation. In this work, we focus on simulating non-unitary parity-time symmetric systems, which exhibit a distinctive symmetry-breaking phase transition as well as other unique features that have no counterpart in closed systems. We show that a qutrit, a three-level quantum system, is capable of realizing this non-equilibrium phase transition. Our results indicate the potential advantage of multi-level (qudit) processors in simulating physical effects, where additional accessible levels can play the role of a controlled environment.
Physical Review Research A 109, 032619 (2024)
arXiv:2310.20432
2023
Quantum Computing for Finance
Quantum computers are expected to surpass the computational capabilities of classical computers during this decade and have transformative impact on numerous industry sectors, particularly finance. In fact, finance is estimated to be the first industry sector to benefit from quantum computing, not only in the medium and long terms, but even in the short term. This survey paper presents a comprehensive summary of the state of the art of quantum computing for financial applications, with particular emphasis on Monte Carlo integration, optimization, and machine learning, showing how these solutions, adapted to work on a quantum computer, can help solve more efficiently and accurately problems such as derivative pricing, risk analysis, portfolio optimization, natural language processing, and fraud detection. We also discuss the feasibility of these algorithms on near-term quantum computers with various hardware implementations and demonstrate how they relate to a wide range of use cases in finance. We hope this article will not only serve as a reference for academic researchers and industry practitioners but also inspire new ideas for future research.
Nature Reviews Physics (2023)
arXiv:2201.02773
Similarity-Based Parameter Transferability in the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm
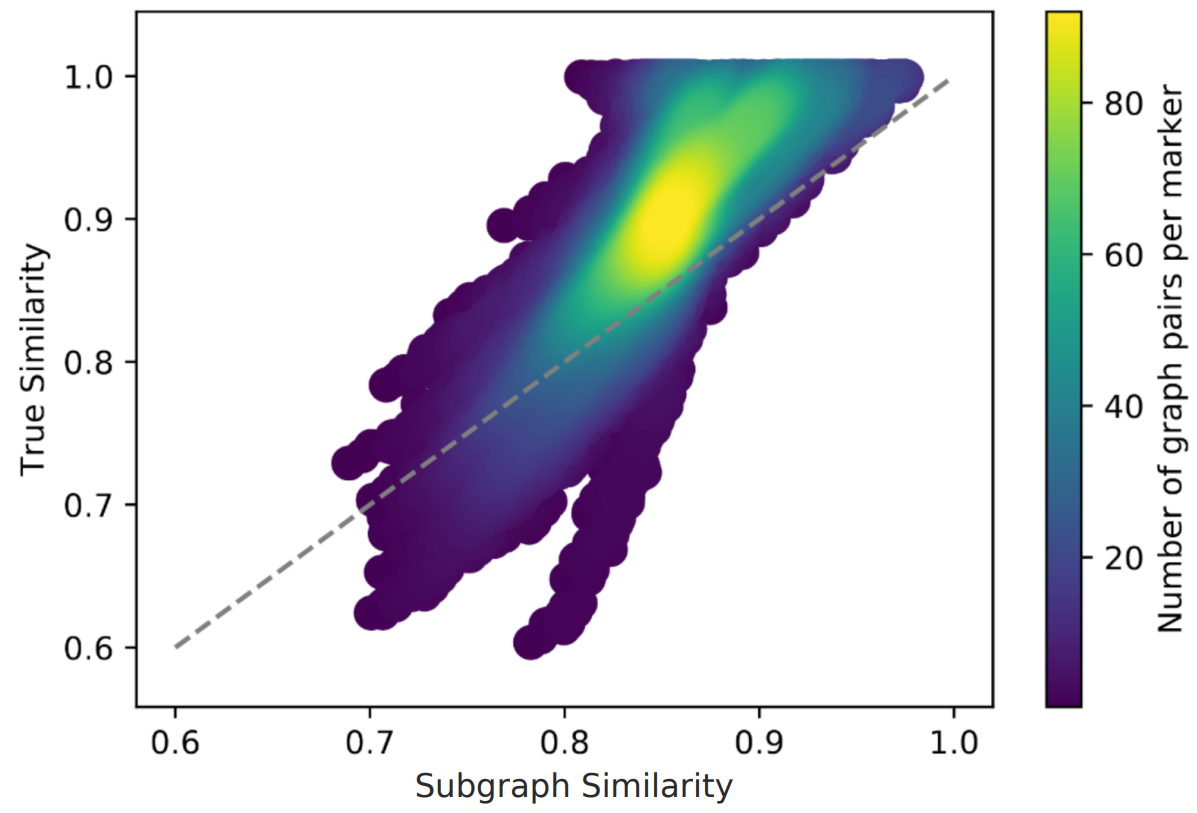
Comparing subgraph similarity metric against the true graph similarity for 12100 graph pairs consisting of 20-node graphs. Linear correlation is observed, with the metric slightly under-approximating the transferability coefficient.
The quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA) is one of the most promising candidates for achieving quantum advantage through quantum-enhanced combinatorial optimization. A near-optimal solution to the combinatorial optimization problem is achieved by preparing a quantum state through the optimization of quantum circuit parameters. Optimal QAOA parameter concentration effects for special MaxCut problem instances have been observed, but a rigorous study of the subject is still lacking. In this work we show clustering of optimal QAOA parameters around specific values; consequently, successful transferability of parameters between different QAOA instances can be explained and predicted based on local properties of the graphs, including the type of subgraphs (lightcones) from which graphs are composed as well as the overall degree of nodes in the graph (parity). We apply this approach to several instances of random graphs with a varying number of nodes as well as parity and show that one can use optimal donor graph QAOA parameters as near-optimal parameters for larger acceptor graphs with comparable approximation ratios. This work presents a pathway to identifying classes of combinatorial optimization instances for which variational quantum algorithms such as QAOA can be substantially accelerated.
Frontiers in Quantum Science and Technology, 2 (2023)
arXiv:2307.05420
Towards a scalable discrete quantum generative adversarial neural network
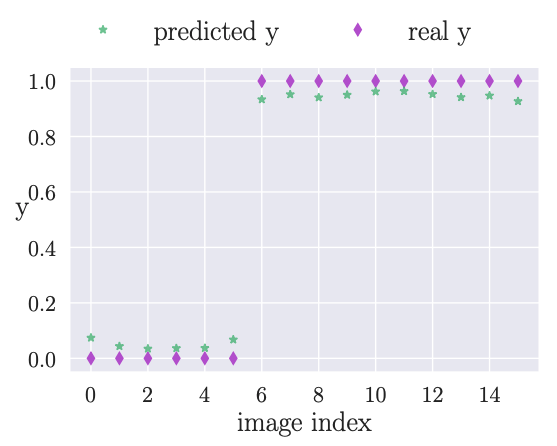
Discriminator on bars & stripes data: the discriminator predictions after training on the dataset with their real labels.
We introduce a fully quantum generative adversarial network intended for use with binary data. The architecture incorporates several features found in other classical and quantum machine learning models, which up to this point had not been used in conjunction. In particular, we incorporate noise reuploading in the generator, auxiliary qubits in the discriminator to enhance expressivity, and a direct connection between the generator and discriminator circuits, obviating the need to access the generator's probability distribution. We show that, as separate components, the generator and discriminator perform as desired. We empirically demonstrate the expressive power of our model on both synthetic data as well as low energy states of an Ising model. Our demonstrations suggest that the model is not only capable of reproducing discrete training data, but also of potentially generalizing from it.
Quantum Science and Technology 8, 035002 (2023)
arXiv:2209.13993
2022
Multibody molecular docking on a quantum annealer
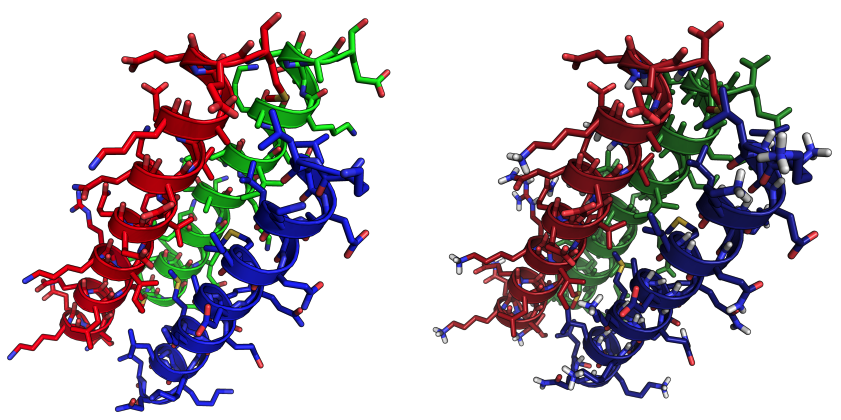
Comparison of actual structure (left) and predicted lowest-energy structure from the quantum annealer (right). The three helices are shown in red, blue, and green respectively, with darker colours for the prediction.
Molecular docking, which aims to find the most stable interacting configuration of a set of molecules, is of critical importance to drug discovery. Although a considerable number of classical algorithms have been developed to carry out molecular docking, most focus on the limiting case of docking two molecules. Since the number of possible configurations of N molecules is exponential in N, those exceptions which permit docking of more than two molecules scale poorly, requiring exponential resources to find high-quality solutions. Here, we introduce a one-hot encoded quadratic unconstrained binary optimization formulation (QUBO) of the multibody molecular docking problem, which is suitable for solution by quantum annealer. Our approach involves a classical pre-computation of pairwise interactions, which scales only quadratically in the number of bodies while permitting well-vetted scoring functions like the Rosetta REF2015 energy function to be used. In a second step, we use the quantum annealer to sample low-energy docked configurations efficiently, considering all possible docked configurations simultaneously through quantum superposition. We show that we are able to minimize the time needed to find diverse low-energy docked configurations by tuning the strength of the penalty used to enforce the one-hot encoding, demonstrating a 3-4 fold improvement in solution quality and diversity over performance achieved with conventional penalty strengths. By mapping the configurational search to a form compatible with current- and future-generation quantum annealers, this work provides an alternative means of solving multibody docking problems that may prove to have performance advantages for large problems, potentially circumventing the exponential scaling of classical approaches and permitting a much more efficient solution to a problem central to drug discovery and validation pipelines.
arXiv:2210.11401
Augmenting QAOA Ansatz with Multiparameter Problem-Independent Layer
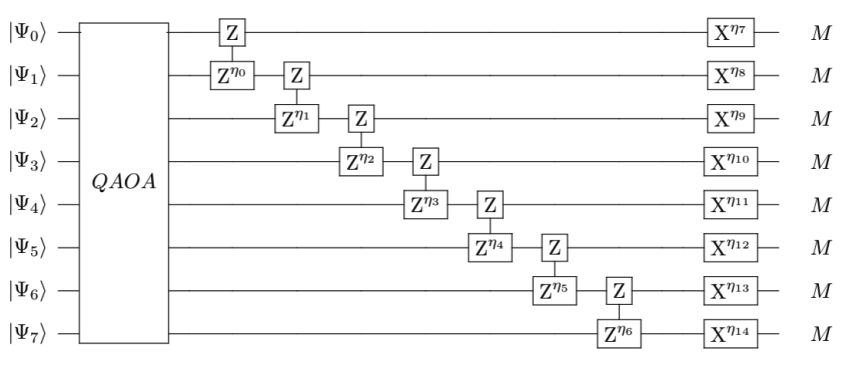
Circuit layout for the alternative QAOA+.
The quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA) promises to solve classically intractable computational problems in the area of combinatorial optimization. A growing amount of evidence suggests that the originally proposed form of the QAOA ansatz is not optimal, however. To address this problem, we propose an alternative ansatz, which we call QAOA+, that augments the traditional p=1 QAOA ansatz with an additional multiparameter problem-independent layer. The QAOA+ ansatz allows obtaining higher approximation ratios than p=1 QAOA while keeping the circuit depth below that of p=2 QAOA, as benchmarked on the MaxCut problem for random regular graphs. We additionally show that the proposed QAOA+ ansatz, while using a larger number of trainable classical parameters than with the standard QAOA, in most cases outperforms alternative multiangle QAOA ansätze.
2022 IEEE QCE, 97 (2022)
arXiv:2205.01192
Characterizing Error Mitigation by Symmetry Verification in QAOA
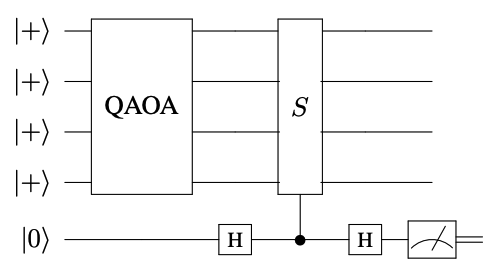
Verification of symmetry S on the QAOA state.
Hardware errors are a major obstacle to demonstrating quantum advantage with the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA). Recently, symmetry verification has been proposed and empirically demonstrated to boost the quantum state fidelity, the expected solution quality, and the success probability of QAOA on a superconducting quantum processor. Symmetry verification uses parity checks that leverage the symmetries of the objective function to be optimized. We develop a theoretical framework for analyzing this approach under local noise and derive explicit formulas for fidelity improvements on problems with global ℤ2 symmetry. We numerically investigate the symmetry verification on the MaxCut problem and identify the error regimes in which this approach improves the QAOA objective. We observe that these regimes correspond to the error rates present in near-term hardware. We further demonstrate the efficacy of symmetry verification on an IonQ trapped ion quantum processor where an improvement in the QAOA objective of up to 19.2\% is observed.
Programming physical quantum systems with pulse-level control
Quantum information processing holds great promise for pushing beyond the current frontiers in computing. Specifically, quantum computation promises to accelerate the solving of certain problems, and there are many opportunities for innovation based on applications in chemistry, engineering, and finance. To harness the full potential of quantum computing, however, we must not only place emphasis on manufacturing better qubits, advancing our algorithms, and developing quantum software. To scale devices to the fault tolerant regime, we must refine device-level quantum control. On May 17-18, 2021, the Chicago Quantum Exchange (CQE) partnered with IBM Quantum and Super.tech to host the Pulse-level Quantum Control Workshop. At the workshop, representatives from academia, national labs, and industry addressed the importance of fine-tuning quantum processing at the physical layer. The purpose of this report is to summarize the topics of this meeting for the quantum community at large.
Experimental high-dimensional Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger entanglement with superconducting transmon qutrits
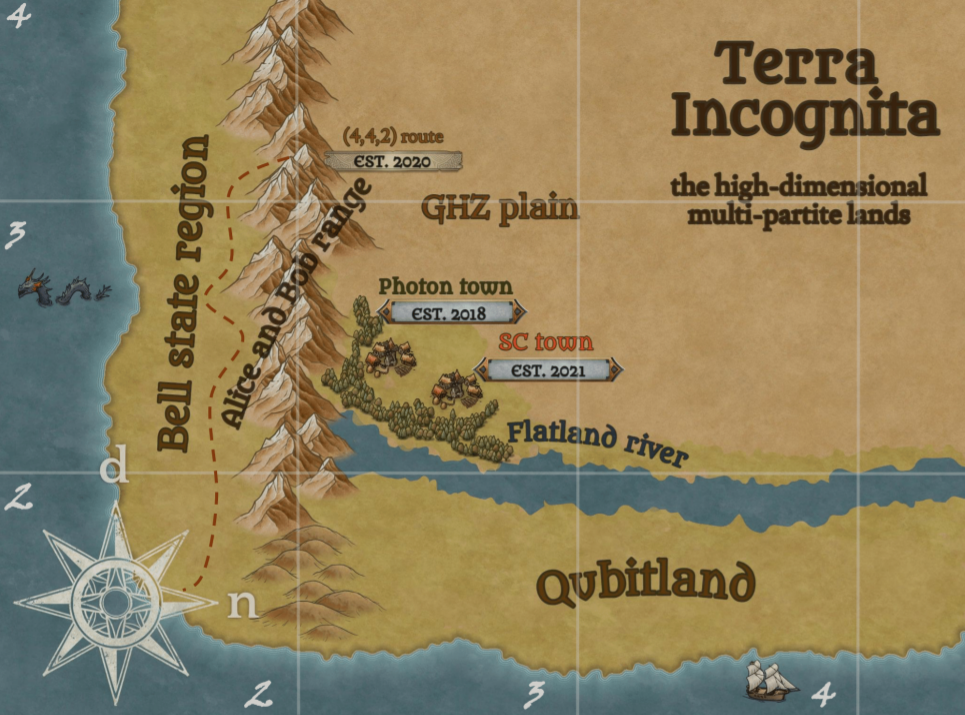
Map of Entangland, representing the experimental state-of-the-art generation of high-dimensional multipartite states.
We report the first experimental demonstration of a high-dimensional multipartite entangled state in a superconducting quantum processor. We generate the three-qutrit Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state by designing the necessary pulses to perform high-dimensional quantum operations. We obtain the fidelity of
78 ± 1%, proving the generation of a genuine three-partite and three-dimensional entangled state.
Branching Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks
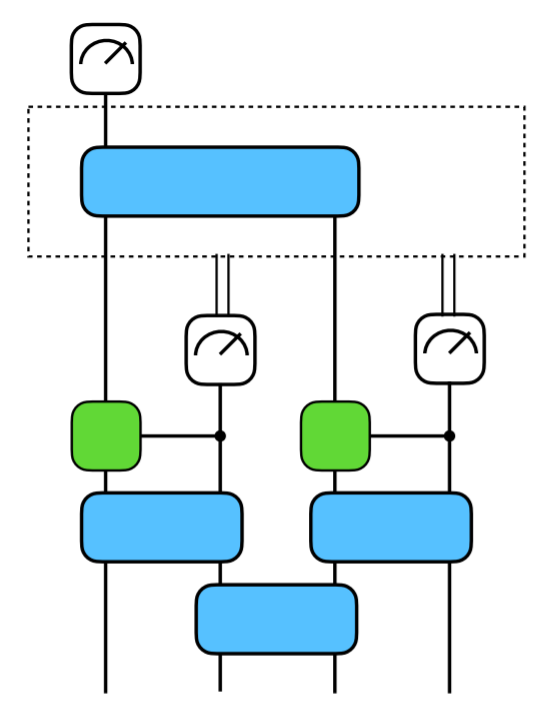
Four-qubit bQCNN containing 111 trainable parameters.
We introduce a new variational circuit ansatz for hybrid quantum machine learning (QML) applications. This ansatz, the branching quantum convolutional neural networks (bQCNN), takes advantage of the merging classical control flow capabilities of quantum devices — that is, their ability to perform mid-circuit measurements and then decide which subsequent quantum operations to execute based on measurement results. Although the bQCNN has the same overall circuit depth as the original QCNN ansatz, it can contain many more trainable parameters, potentially increasing the range of QML tasks that can be performed on NISQ devices, where circuit depth is inherently limited by gate errors.
2021
Simulating Large PEPs Tensor Networks on Small Quantum Devices
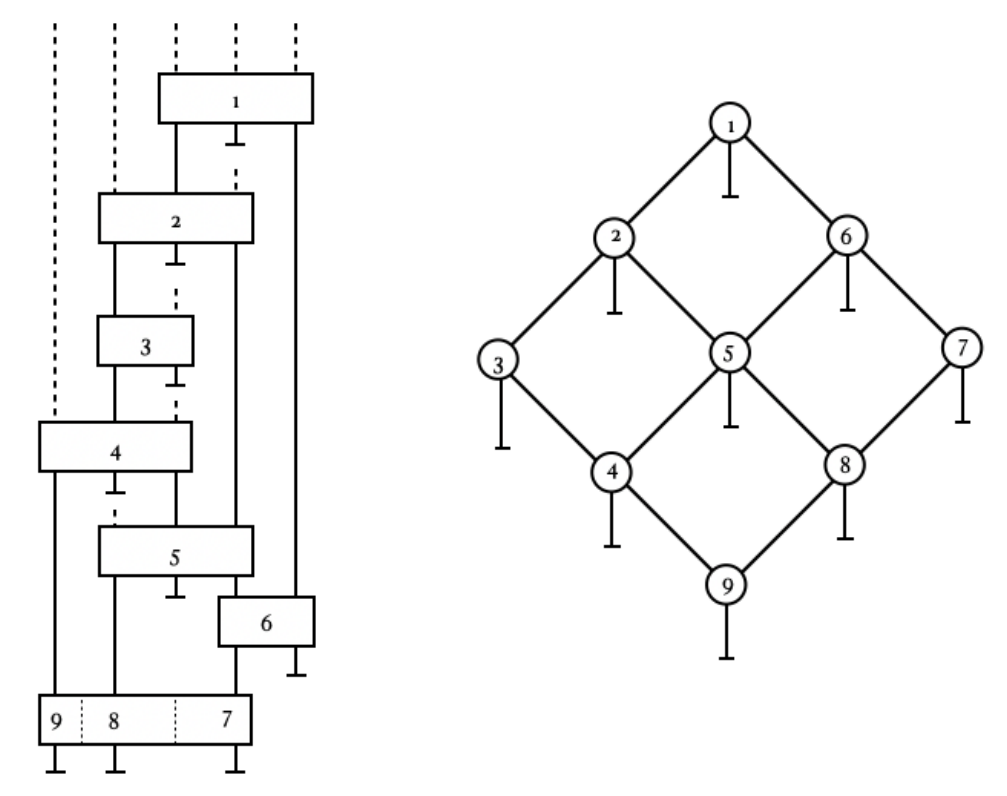
5-qubit quantum circuit (left) corresponding to the 9-qubit PEPs tensor network (right).
We systematically map low-bond-dimension PEPs tensor networks to quantum circuits. By measuring and reusing qubits, we demonstrate that a simulation of an N × M square-lattice PEPs network, for arbitrary M, of bond dimension 2 can be performed using N + 2 qubits. We employ this approach to calculate the values of a long-range loop observable in the topological Wen plaquette model by mapping a 3 × 3 PEPs tensor network to a 5-qubit quantum circuit and executing it on the Honeywell System Model H1-1 trapped-ion device. We find that, for this system size, the noisy observable values are sufficient for diagnosing topological vs. trivial order, as the Wen model is perturbed by a magnetic field term in the Hamiltonian. Our results serve as a proof-of-concept of the utility of the measure-and-reuse approach for simulating large two-dimensional quantum systems on small quantum devices.
arXiv:2110.00507
Implementing a Ternary Decomposition of the Toffoli Gate on Fixed-Frequency Transmon Qutrits
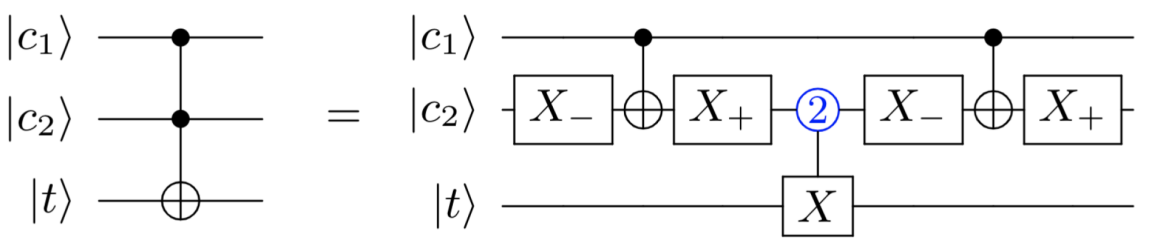
Qutrit decomposition of a Toffoli quantum gate.
Most quantum devices naturally have multiple accessible energy levels beyond the lowest two traditionally used to define a qubit. Here, we experimentally demonstrate a ternary decomposition of a multi-qubit operation on cloud-enabled fixed-frequency superconducting transmons. Specifically, we realize an order-preserving Toffoli gate consisting of four two-transmon operations, whereas the optimal order-preserving binary decomposition uses eight CNOTs on a linear transmon topology. Both decompositions are benchmarked via truth table fidelity where the ternary approach outperforms on most sets of transmons on ibmq_jakarta, and is further benchmarked via quantum process tomography on one set of transmons to achieve an average gate fidelity of 78.00% ± 1.93%.
arXiv:2109.00558
Transferability of QAOA Parameters between Random Graphs
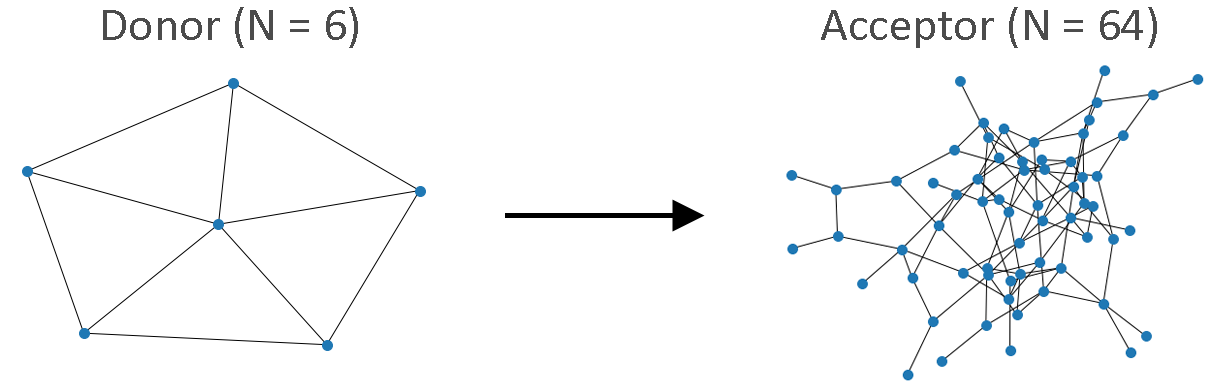
Demonstration of optimized parameter transferability between N = 6 donor and N = 64 acceptor random graphs.
We show that convergence of the optimal QAOA parameters around specific values and, consequently, successful transferability of parameters between different QAOA instances can be explained and predicted based on the local properties of the graphs, specifically the types of subgraphs (lightcones) from which the graphs are composed. We apply this approach to random regular and general random graphs. For example, we demonstrate how optimized parameters calculated for a 6-node random graph can be successfully used without modification as nearly optimal parameters for a 64-node random graph, with 0.8% reduction in approximation ratio as a result.
Error Mitigation for Deep Quantum Optimization Circuits by Leveraging Problem Symmetries
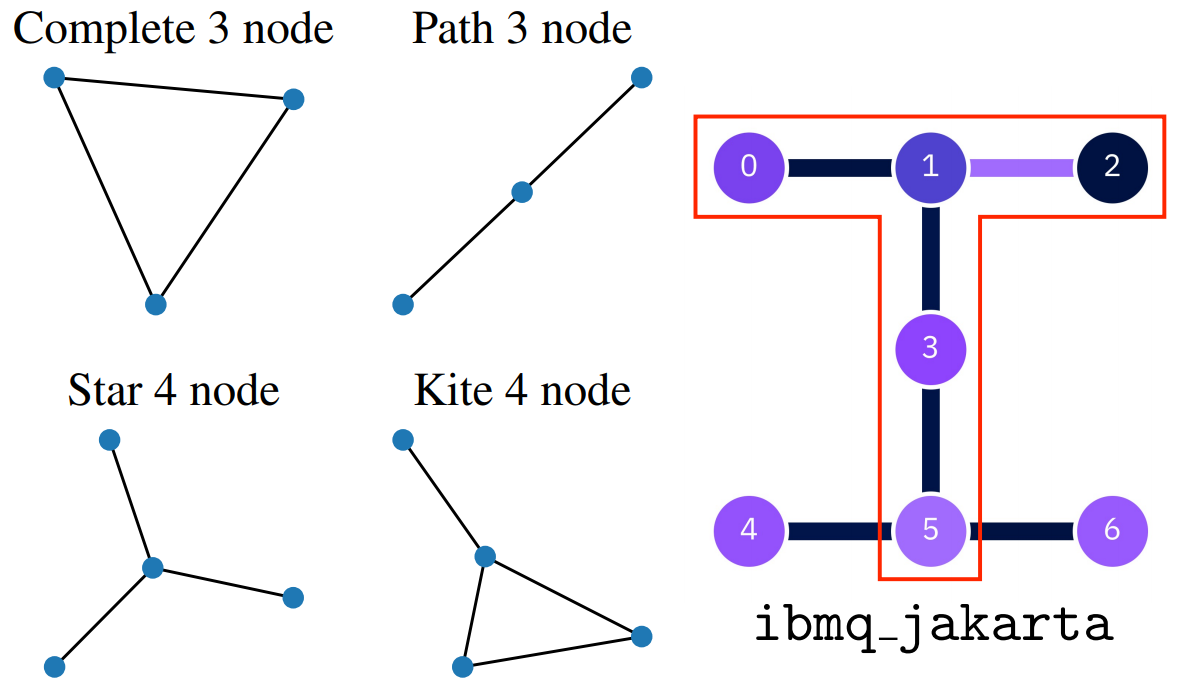
Graphs for the MaxCut instances considered and the ibmq_jakarta layout. The qubits used in experiments are highlighted in red.
We introduce an application specific approach for mitigating the errors in QAOA evolution by leveraging the symmetries present in the classical objective function to be optimized. Specifically, the QAOA state is projected into the symmetry-restricted subspace, with projection being performed either at the end of the circuit or throughout the evolution. Our approach improves the fidelity of the QAOA state, thereby increasing both the accuracy of the sample estimate of the QAOA objective and the probability of sampling the binary string corresponding to that objective value. We experimentally verify the proposed methods on an IBM Quantum processor, utilizing up to 5 qubits. When leveraging a global bitflip symmetry, our approach leads to a 23% average improvement in quantum state fidelity.
Error rate reduction of single-qubit gates via noise-aware decomposition into native gates
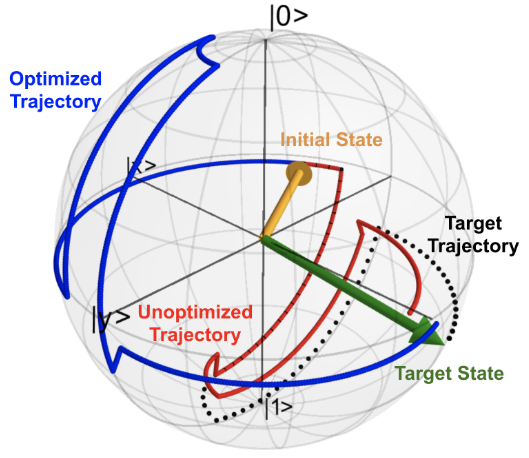
Optimized and unoptimized single-qubit gate trajectories mapped through the Bloch sphere in the presence of aggerated noise.
We introduce an approach by which knowledge of a qubit’s initial quantum state and the standard parameters describing its decoherence can be leveraged to mitigate the noise present during the execution of a single-qubit gate. We benchmark our protocol using cloud-based access to IBM quantum hardware and demonstrate a reduction of the single-qubit error rate by 38%. The protocol can be used to reduce quantum state preparation errors, as well as to improve the fidelity of quantum circuits for which some knowledge of the qubits’ intermediate states can be inferred. This work presents a pathway to using information about noise levels and quantum state distributions to significantly reduce error rates associated with quantum gates via optimized decomposition into native gates.
Demonstration of quantum advantage by a joint detection receiver for optical communications using quantum belief propagation on a trapped-ion device
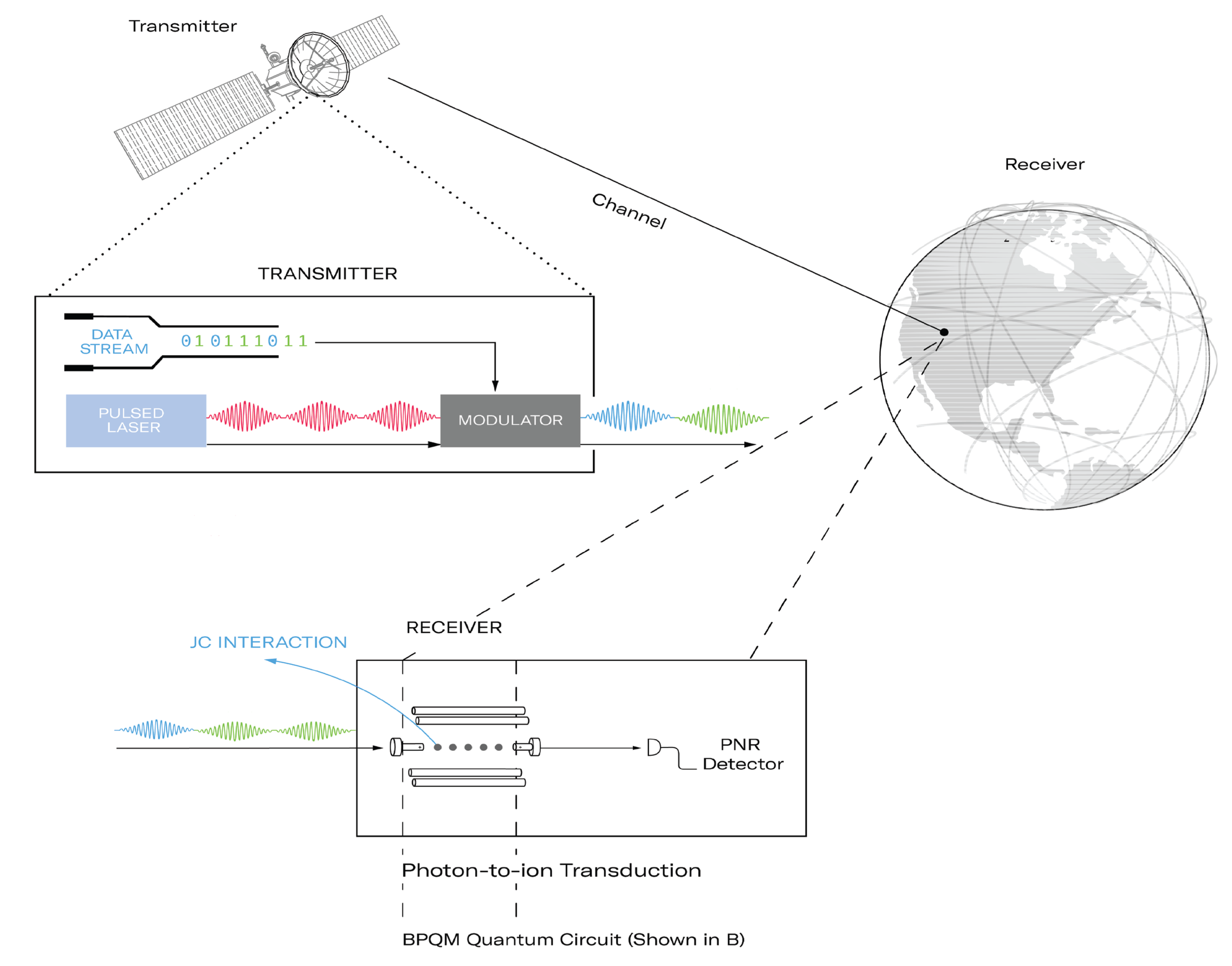
Schematic heat flow diagram of graphene Cooper pair splitter device.
We conclusively realize a previously postulated joint quantum detection scheme on a trapped-ion quantum device, and show an experimental framework to surpass the quantum limit on the minimum average decoding error probability in the low-photon limit by leveraging a combination of mid-circuit measurement-enabled experiments, the connectivity of trapped-ion devices, and a mapping of the relevant photonic coherent states onto inner product preserving single qubit states.
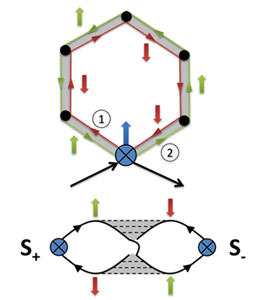
Thermoelectric current in a graphene Cooper pair splitter
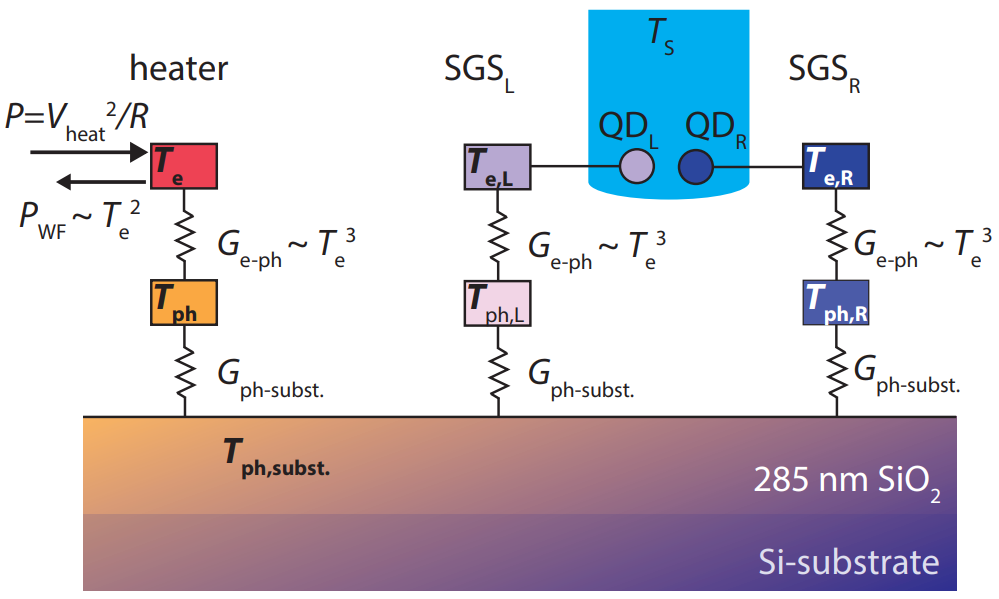
Schematic heat flow diagram of graphene Cooper pair splitter device.
Thermoelectric effect generating electricity from thermal gradient and vice versa appears in numerous generic applications. Recently, an original prospect of thermoelectricity arising from the nonlocal Cooper pair splitting (CPS) and the elastic co-tunneling in hybrid normal metal-superconductor-normal metal structures was foreseen. Here we demonstrate experimentally the existence of non-local Seebeck effect in a graphene-based CPS device comprising two quantum dots connected to an aluminum superconductor and theoretically validate the observations. This non-local Seebeck effect offers an efficient tool for producing entangled electrons.
2020
Tensor Network Quantum Simulator With Step-Dependent Parallelization
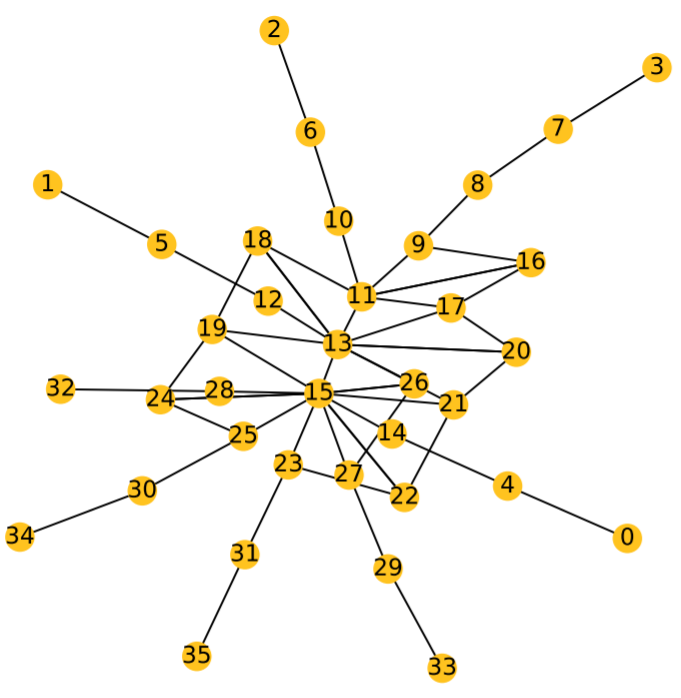
Graph representation of tensor expression of a QAOA circuit.
We present a new large-scale quantum circuit simulator based on the tensor network contraction technique to represent quantum circuits. We propose a novel parallelization algorithm based on step-dependent slicing and push the requirement on the size of a quantum computer that will be needed to demonstrate the advantage of quantum computation with Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA).
Strong coupling-enabled broadband non-reciprocity
On-chip signal transmission in both classical and quantum regimes desires broadband nonreciprocity to overcome signal instabilities.
Non-reciprocity of signal transmission enhances capacity of communication channels and protects transmission quality against possible signal instabilities, thus becoming an important component ensuring coherent information processing. However, non-reciprocal transmission requires breaking time-reversal symmetry, which poses challenges of both practical and fundamental character hindering the progress. Here we report an alternative scheme for achieving broadband nonreciprocity using a specially engineered hybrid microwave cavity.
Physical Review Applied 13, 044039 (2020)
Featured as Editor’s Suggestion
Controllable skyrmion chirality in ferroelectrics
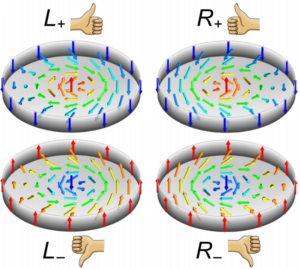
Four types of the skyrmions, differing by their chirality and polarity. The hand pictograms define the classification of the skyrmions.
Chirality, an intrinsic handedness, is one of the most intriguing fundamental phenomena in nature. Materials composed of chiral molecules find broad applications in areas ranging from nonlinear optics and spintronics to biology and pharmaceuticals. However, chirality is usually an invariable inherent property of a given material that cannot be easily changed at will. Here, we demonstrate that ferroelectric nanodots support skyrmions the chirality of which can be controlled and switched. We devise protocols for realizing control and efficient manipulations of the different types of skyrmions. Our findings open the route for controlled chirality with potential applications in ferroelectric-based information technologies.
2019 and older
Exceptional points in classical spin dynamics
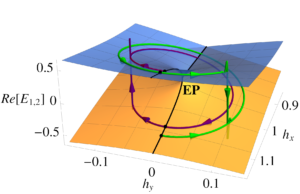
Parametric trajectories going around the EP in opposite directions, illustrating nonreciprocity of non-Hermitian parametric driving
Building on the remarkable recent progress in understanding the parity-time-symmetric dynamics in spin systems, we use the topological properties of exceptional points (EPs) to implement chiral non-reciprocal transmission of a spin through a material with non-uniform magnetization, like helical magnet. We consider an exemplary system, spin-torque-driven single spin described by a time-dependent non-Hermitian Hamiltonian. We show that encircling individual EPs in a parameter space results in non-reciprocal spin dynamics and find the range of optimal protocol parameters for high-efficiency operation of asymmetric spin filter device based on this effect.
Parity-time symmetry breaking in spin chains
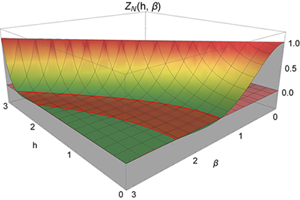
Partition function of PT-symmetric Heisenberg spin chain with Lee-Yang zeros in the regime of broken PT symmetry.
We investigate nonequilibrium phase transitions in classical Heisenberg spin chains associated with spontaneous breaking of PT symmetry under the action of Slonczewski spin-transfer torque (STT). We reveal STT-driven PT symmetry-breaking phase transition between the regimes of precessional and exponentially damped spin dynamics. The physical interpretation of imaginary magnetic field as describing the action of nonconservative forces opens the possibility
of direct observations of Lee-Yang zeros in nonequilibrium physical systems.
Fluctuation spectroscopy: From Rayleigh-Jeans waves to Abrikosov vortex clusters
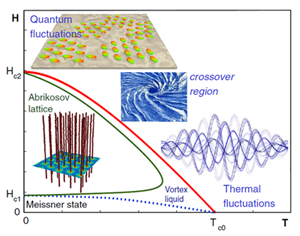
Schematic phase diagram of type-II superconductors, showing the domains of qualitatively different physical behavior.
We review the physics of superconducting fluctuations, commencing from a qualitative description of thermodynamic fluctuations close to the critical temperature and quantum fluctuations at zero temperature in the vicinity of the second critical field. The analysis of the latter allows us to present fluctuation formation as a fragmentation of the Abrikosov lattice. This review highlights a series of experimental findings followed by microscopic description and numerical analysis of the effects of fluctuations on numerous properties of superconductors in the entire phase diagram and beyond the superconducting phase.
Scaling universality at the dynamic vortex Mott transition
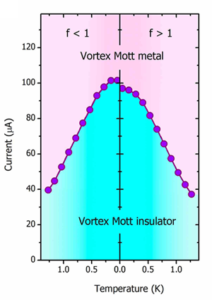
Temperature-current phase diagram of the vortex Mott states.
We report the critical behavior of a system of superconducting vortices as it experiences the dynamic Mott insulator-to-metal transition, driven by either current or temperature. We find universal scaling with respect to both, expressed by the same scaling function and characterized by a single critical exponent coinciding with the exponent for the thermodynamic Mott transition. We develop a theory for the phase transition based on the parity reflection-time reversal (PT) symmetry-breaking formalism and find that the nonequilibrium-induced Mott transition has the same critical behavior as the thermal Mott transition. Our findings demonstrate the existence of physical systems in which the effect of a nonequilibrium drive is to generate an effective temperature and, hence, the transition of the thermal universality class.
Linear dynamics of classical spin as Möbius transformation
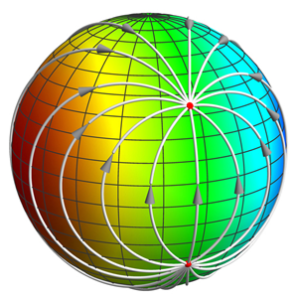
Non-conservative spin dynamics conrresponding to loxodromic Möbius transformation.
We have shown that non-conservative dynamics of a linear spin system has a simple interpretation in terms of Möbius transformations of the complex plane. The parity-time symmetry-breaking phase transition is identified as a transition between elliptic and hyperbolic (via parabolic) classes of Möbius transformations.
Nature Scientific Reports 7, 1168 (2017)
Universality and critical behavior of the dynamical Mott transition in a system with long-range interactions
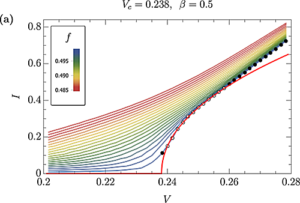
Dynamics vortex Mott metal-insulator transition.
We study numerically the voltage-induced breakdown of a Mott insulating phase in a system of charged classical particles with long-range interactions. At half-filling on a square lattice this system exhibits Mott localization in the form of a checkerboard pattern. We find universal scaling behavior of the current at the dynamic Mott insulator-metal transition and calculate scaling exponents corresponding to the transition. Our results are in agreement, up to a difference in universality class, with recent experimental evidence of a dynamic Mott transition in a system of interacting superconducting vortices.
Nature Scientific Reports 7, 44044 (2017)
Parity-time symmetry breaking in magnetic systems
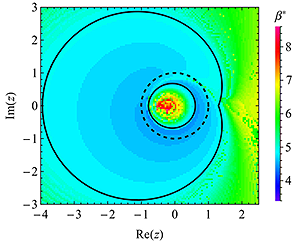
Micromagnetic simulations confirming PT-symmetry breaking.
In this work we show that non-equilibrium dynamics of a single classical spin (monodomain ferromagnet), usually described by the Landau-Lifshitz-Slonczewski equation, can be derived using the generalized non-Hermitian Hamiltonian formalism. This is the first application of this novel approach to magnetic systems. The anti-Hermitian part of the proposed spin Hamiltonian is responsible for non-conservative forces (Gilbert damping and Slonczewski spin-transfer torque). Parity-time (PT) symmetry-breaking phase transition was predicted and verified numerically.
Parity-time symmetry-breaking mechanism of dynamic Mott transitions in dissipative systems
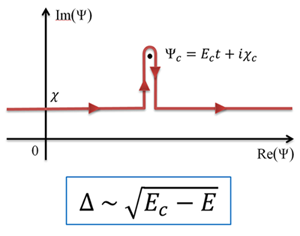
Integration contour in the complex plane for calculating the Landau-Zener-Schwinger transition probability.
We describe the critical behavior of the electric field-driven (dynamic) Mott insulator-to-metal transitions in dissipative Fermi and Bose systems in terms of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians invariant under simultaneous parity (P) and time-reversal (T ) operations. The dynamic Mott transition is identified as a PT symmetry-breaking phase transition, with the Mott insulating state corresponding to the regime of unbroken PT symmetry with a real energy spectrum. We establish that the imaginary part of the Hamiltonian arises from the combined effects of the driving field and inherent dissipation. We derive the renormalization and collapse of the Mott gap at the dielectric breakdown and describe the resulting critical behavior of transport characteristics. The obtained critical exponent is in an excellent agreement with experimental findings.
Effect of fluctuations on the NMR relaxation beyond the Abrikosov vortex state
Maki-Thompson relaxation process.
In this work we investigate the important role of the Maki-Thompson quantum process of electron `self-pairing' on self-intersecting trajectories involving spin-flip processes. This effect increases NMR relaxation rate in two-dimensional superconductors above the critical temperature. Due to the competing effect of suppression of particle density of states, different scenarios of NMR rate dependence on temperature and magnetic field become possible.
Resonant tunneling of fluctuation Cooper pairs
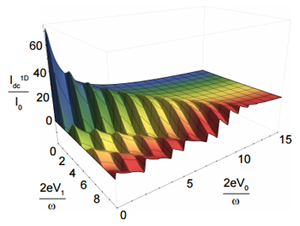
Resonant Shapiro spikes in tunneling dc current of fluctuation Cooper pairs.
Here we predict a novel fluctuation phenomenon: resonant tunneling of superconducting fluctuations across a Superconductor-Insulator-Superconductor junction above superconducting critical temperature. This new effect provides the first direct tool of measuring lifetime of fluctuation Cooper pairs and marks a radical departure from the conventional view of superconducting fluctuations as blurring and rounding phenomenon.
Nature Scientific Reports 5, 8315 (2015)
Featured as Editor’s Suggestion, DoE Science Headlines, and Argonne's Feature Stories
